再熟悉一下SQL的一些操作
临入职之前再熟悉下SQL的一些操作。
发现chatgpt是挺好用的,找解题方法还是找bug,都还行。就是不知实际场景遇到问题可不可行了,有待测试。网址先放这:链接
LIKE
'%a' //以a结尾的数据
'a%' //以a开头的数据
'%a%' //含有a的数据
'_a_' //三位且中间字母是a的
'_a' //两位且结尾字母是a的
'a_' //两位且开头字母是a的
数据表
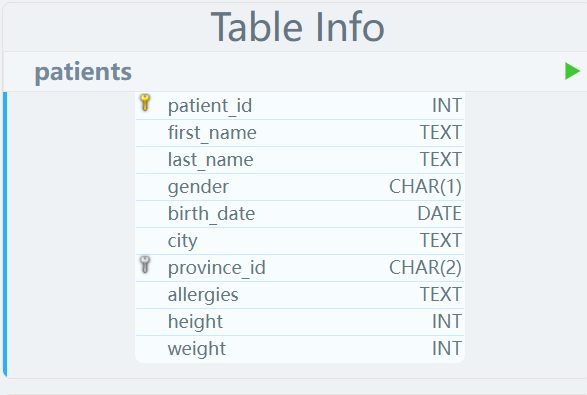
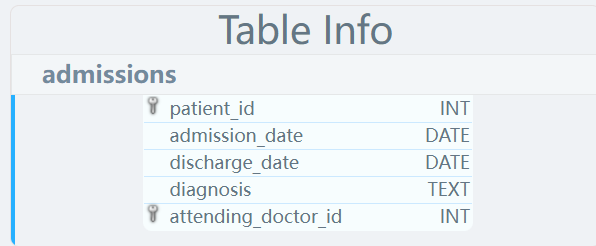
LIKE _
Show patient_id and first_name from patients where their first_name start and ends with 's' and is at least 6 characters long.
solution:
SELECT patient_id,first_name
FROM patients
where first_name like 's____%s';
CASE WHEN
Show the total amount of male patients and the total amount of female patients in the patients table.
Display the two results in the same row.
解:
SELECT
(select COUNT(1) FROM patients where gender = 'M') AS male_count,
(select COUNT(1) FROM patients where gender = 'F') AS female_count;
SELECT
SUM(gender='M') AS male_count,
SUM(gender='F') AS female_count
from patients;
SELECT
SUM(CASE WHEN gender='M'THEN 1 END) AS male_count,
SUM(CASE WHEN gender='F' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS female_count
from patients;
GROUP BY
GROUP BY 语句根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组。
在分组的列上我们可以使用 COUNT, SUM, AVG,等函数。
Show patient_id, diagnosis from admissions. Find patients admitted multiple times for the same diagnosis.
解:
SELECT patient_id,diagnosis
FROM admissions
group by patient_id,diagnosis
having count(diagnosis)>1;
UNION ALL
SQL UNION 操作符合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果。
UNION 内部的每个 SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列。列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。同时,每个 SELECT 语句中的列的顺序必须相同。
UNION 操作符选取不同的值。如果允许重复的值,请使用 UNION ALL。
SELECT first_name, last_name, 'Patient' as role FROM patients
union all
select first_name, last_name, 'Doctor' from doctors;
MAX
Show all columns for patient_id 542's most recent admission_date.
select *
from admissions
where patient_id=542
and admission_date=(
select max(admission_date) from admissions where patient_id=542);
或者:
SELECT *
FROM admissions
WHERE patient_id = 542
GROUP BY patient_id
HAVING
admission_date = MAX(admission_date);
统计
Each admission costs $50 for patients without insurance, and $10 for patients with insurance. All patients with an even patient_id have insurance.
Give each patient a 'Yes' if they have insurance, and a 'No' if they don't have insurance. Add up the admission_total cost for each has_insurance group.
SELECT (CASE WHEN patient_id%2==0 THEN "Yes" ELSE "No" END) AS has_insurance,
SUM(case when patient_id%2==0 THEN 10 ELSE 50 END) AS admission_total
FROM admissions
group by has_insurance;

除法
求gender为M的百分比
SELECT
round(100 * avg(gender = 'M'), 2) || '%' AS percent_of_male_patients
FROM
patients;
SELECT
CONCAT(ROUND(SUM(gender='M') / CAST(COUNT(*) AS float), 4) * 100, '%')
FROM patients;
== LAG ==
For each day display the total amount of admissions on that day. Display the amount changed from the previous date.
SELECT
admission_date,
COUNT(*) as total_admissions,
COUNT(*) - LAG(COUNT(*)) OVER (ORDER BY admission_date) as change_from_previous_day
FROM
admissions
GROUP BY
admission_date
ORDER BY
admission_date;
ORDER BY
Sort the province names in ascending order in such a way that the province 'Ontario' is always on top.
