Netty概述
Netty是一个JBoss提供的Java开源框架,提供异步、事件驱动的网络应用程序框架和工具。可以快速简单开发出一个网络应用,例如实现某种协议的服务端/客户端应用。JBoss:在J2EE应用服务器领域,JBoss是发展最为迅速的应用服务器。Netty 对 JDK 自带的 NIO 的 API 进行了封装。
Java NIO
介绍
一般认为是non-blocking io。
面向缓冲区。数据读取到稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时读。
三大核心:Channel、Buffer、Selector。
Channel、Buffer、Selector关系图如下:
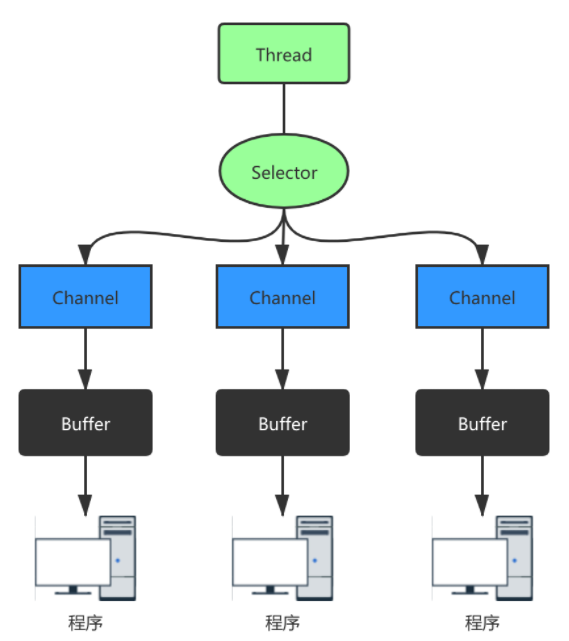
一个Channel对应一个buffer,selector对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个channel,上图有三个channel注册到selector,切换到哪个channel由事件决定。buffer是一个内存块,底层有一个数组。
缓冲区buffer
Buffer例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntBuffer buffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
for(int i=0;i<buffer.capacity();i++) {
buffer.put(i);
}
buffer.flip(); // 翻转读写模式
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println(buffer.get());
}
}
Buffer类是一个抽象类,下面有具体的实现。
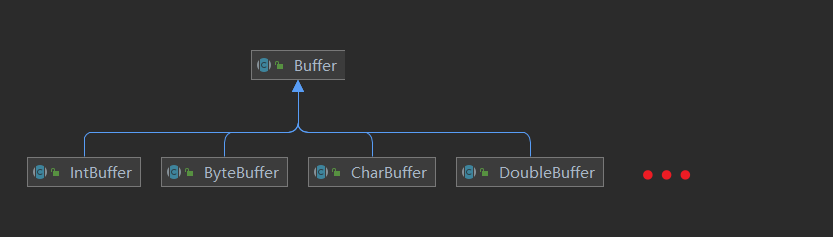
示意图:
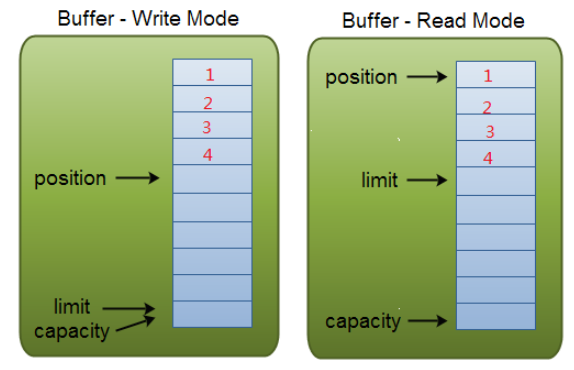
capacity:在读/写模式下都是固定的,就是我们分配的缓冲大小(容量)。
position:类似于读/写指针,表示当前读(写)到什么位置。
limit:在写模式下表示最多能写入多少数据,此时和capacity相同。在读模式下表示最多能读多少数据,此时和缓存中的实际 数据大小相同。
通道Channel
NIO通道类似流,区别:通道可以同时读写,可以异步读写,可以缓冲区读写。
Channel 在 NIO 中是一个接口 public interface Channel extends Closeable{}。常用的 Channel 类有: FileChannel、DatagramChannel、ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 。
【ServerSocketChanne 类似 ServerSocket、SocketChannel 类似 Socket】
FileChannel 用于文件的数据读写,DatagramChannel 用于 UDP 的数据读写,ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 用于 TCP 的数据读写。
FileChannel
写入本地文件:
public class FileChan {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "cn.orzlinux";
//创建输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\PC\\Desktop\\hqinglau.txt");
//转换为FileChannel
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//str放入缓冲区
buffer.put(str.getBytes());
//转换为读模式
buffer.flip();
//buffer写入fileChannel
fileChannel.write(buffer);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
结果:

读取本地文件:
public class FileChan {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\PC\\Desktop\\hqinglau.txt");
//创建输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//转换为FileChannel
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
//放入缓冲区
fileChannel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array())); // cn.orzlinux
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
文件拷贝:可以通过连续读取到缓冲区然后写入文件的方法,或者FileChannel的transferFrom方法。
public class FileChan {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\PC\\Desktop\\hqinglau.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\PC\\Desktop\\hqinglau2.txt");
FileChannel sourceChan = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destChan = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
destChan.transferFrom(sourceChan,0,sourceChan.size());
sourceChan.close();
destChan.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
Buffer和Channel的一些细节
得到一个只读的buffer
//得到一个只读的 Buffer
ByteBuffer readOnlyBuffer = buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
再放入会报错ReadOnlyBufferException。
内存中修改文件
NIO 提供了 MappedByteBuffer,可以让文件直接在内存中进行修改,而如何同步到文件由 NIO 来完成。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("C:\\Users\\PC\\Desktop\\hqinglau.txt","rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
// mode position size
MappedByteBuffer buffer = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE,0,5);
buffer.put(0, (byte) 'Y');
buffer.put(3, (byte) 'D');
buffer.put(5, (byte) 'I'); // 超界
// cn.orzlinux -> Yn.Drzlinux
randomAccessFile.close();
}
Buffer数组读写操作
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(9999);
// 端口绑定
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
int messageLen = 8; // 从客户端接收8字节
while (true) {
int byteRead = 0;
while (byteRead < messageLen) {
// here
long l = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
if(l<=0) {
continue;
}
byteRead += l;
System.out.println("byteRead = " + byteRead);
Arrays.stream(byteBuffers)
.map(buffer -> "position = " + buffer.position() + ", limit = " + buffer.limit())
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//将所有的 buffer 进行 flip
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::flip);
//将数据读出显示到客户端
long byteWirte = 0;
while (byteWirte < messageLen) {
long l = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWirte += l;
}
//将所有的buffer进行clear
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::clear);
System.out.println("byteRead = " + byteRead + ", byteWrite = " + byteWirte + ", messagelength = " + messageLen);
}
}
选择器Selector
类似epoll
Netty
NIO使用比较复杂。开发难度大,某些版本有Bug。Netty 对 JDK 自带的 NIO 的 API 进行了封装,解决了上述问题。
传统阻塞IO服务模型
采用阻塞IO获取输入数据,每个链接独立线程处理。并发数大时,占用大量系统资源。无数据可读时会阻塞。
Reactor模式
IO复用模型,多个连接共用一个阻塞对象,无需阻塞等待所以连接。某个连接有数据可以处理时,操作系统通知应用。
线程池,复用线程资源。
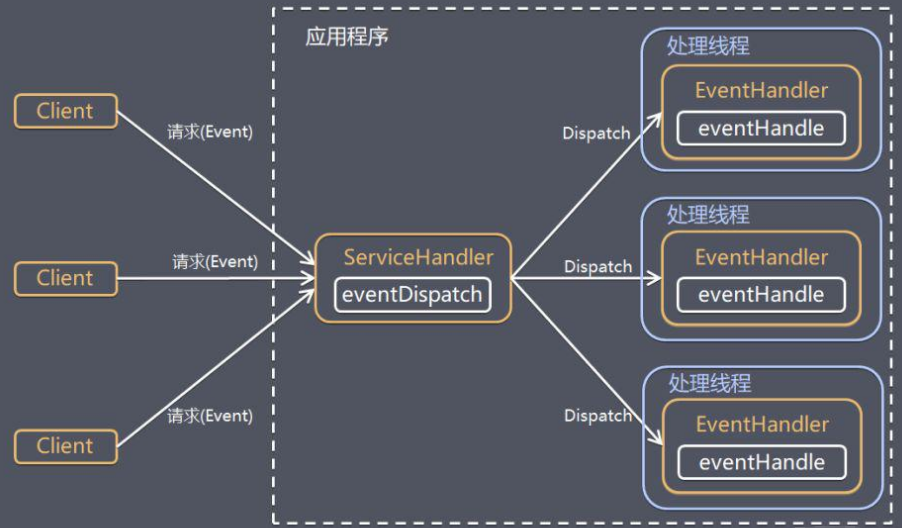
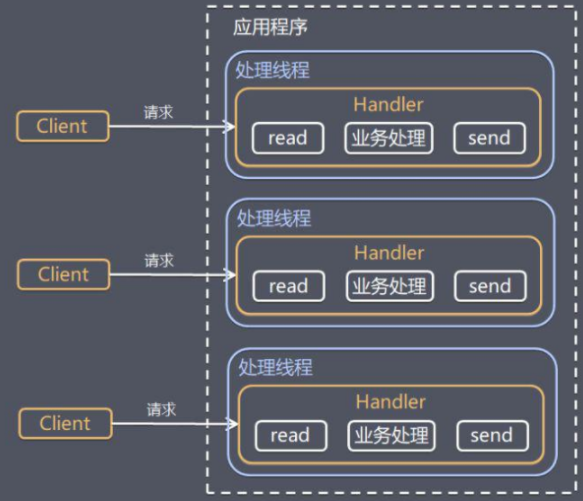
单Reactor多线程
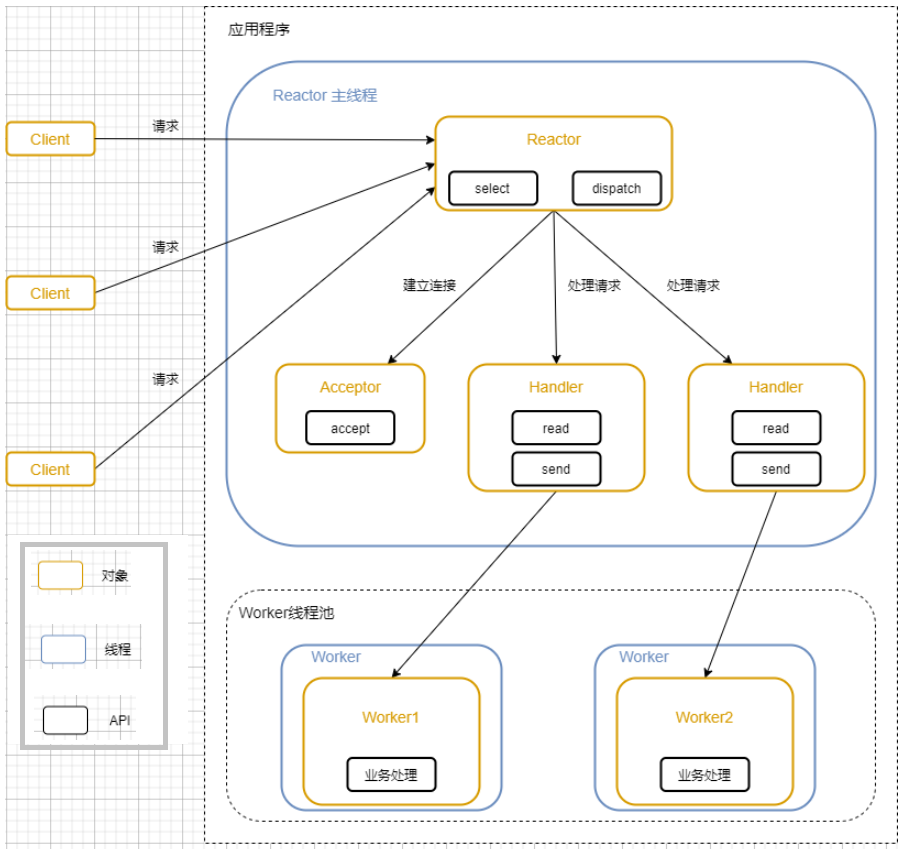
Reactor对象通过select监听客户端请求,收到事件后进行分发。如果是处理请求分配给worker线程池处理。Handler只负责响应,不做业务处理。
优点:可以利用多核CPU的处理能力。
主从Reactor模式
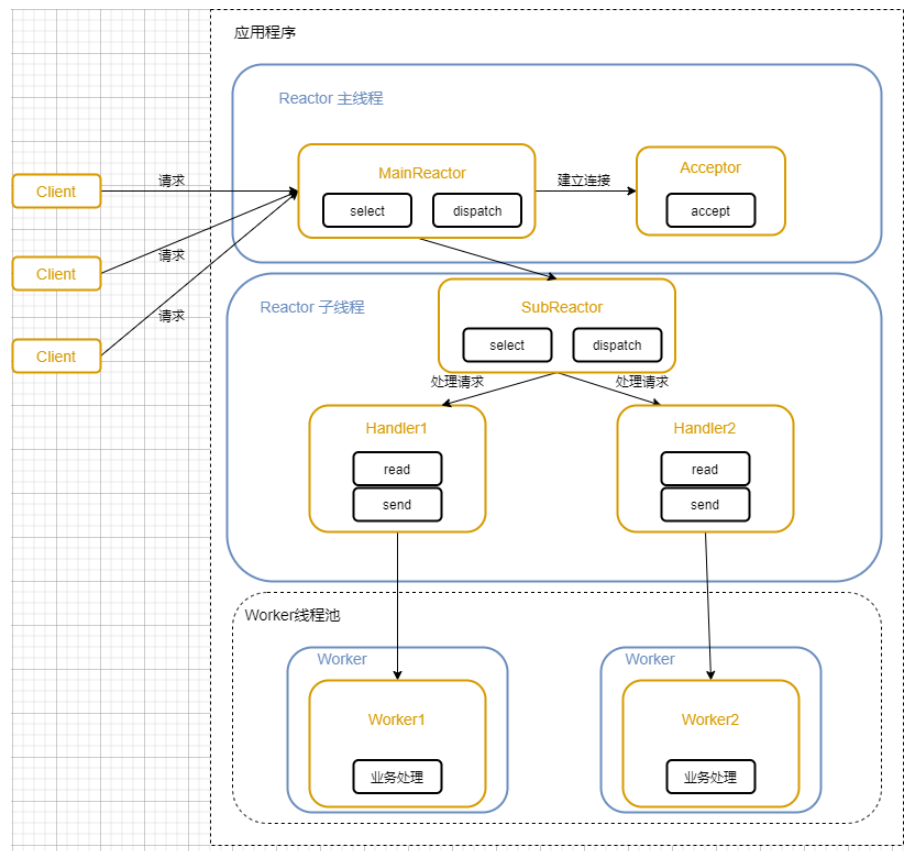
处理请求分配给SubReactor,SubReactor将连接加入到连接队列进行监听。
父线程与子线程的数据交互简单职责明确,父线程只需要接收新连接,子线程完成后续的业务处理。父线程与子线程的数据交互简单,Reactor 主线程只需要把新连接传给子线程,子线程无需返回数据。
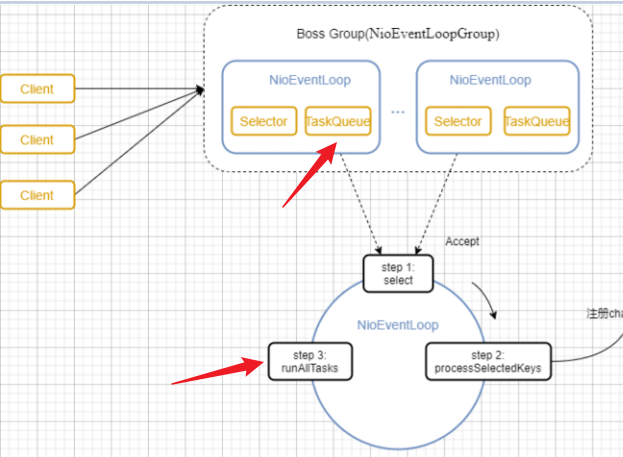
Netty模型
将Reactor的多线程模型改进为多个Reactor。
详细示意图:
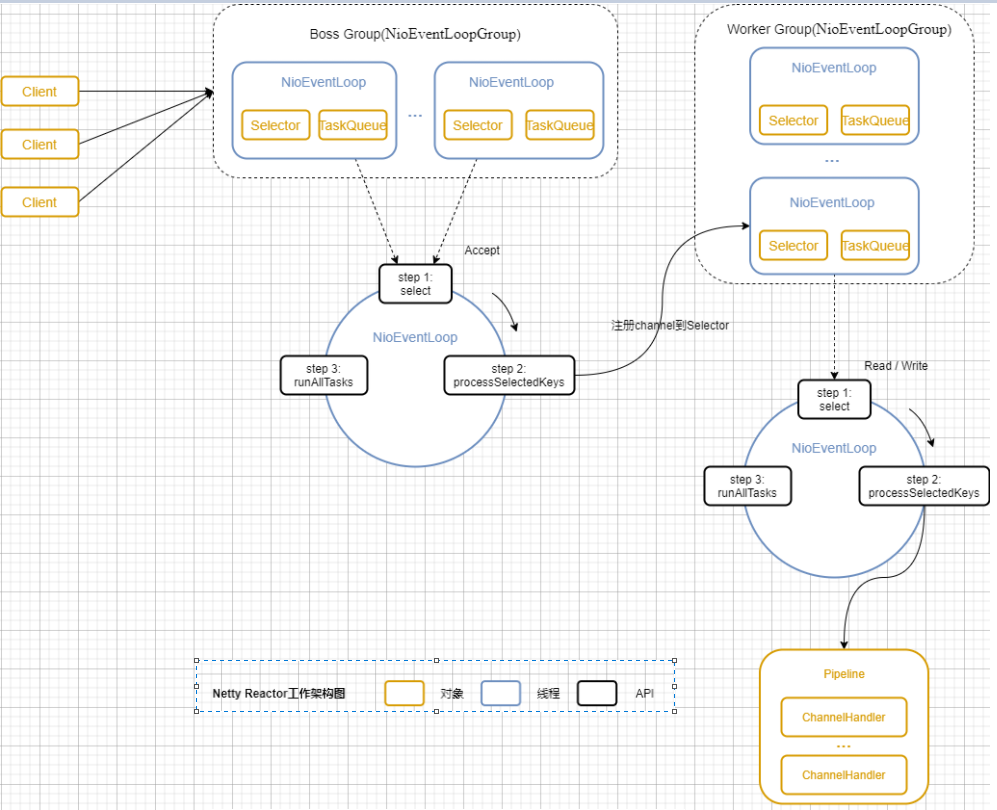
BossGroup负责接收客户端连接,WorkerGroup负责网络读写。都是NIOEventLoopGroup。
其中有多个NioEventLoop。每个NioEventLoop表示一个任务处理线程,有一个selector,负责监听绑定在其上的socket的网络通信。
Boss NioEventLoop:轮询accept,处理,与client建立连接,生成channel,注册到某个Worker NioEventLoop上,处理任务队列的任务。
Worker NioEventLoop:轮询read,write,处理IO事件,处理任务队列。
Worker NioEventLoop处理业务时,会使用pipeline,包含了channel,还维护了很多handler处理器。
echo例子
项目中建两个module,目录如下:
EchoServer.java:
package cn.orzlinux.server;
import cn.orzlinux.server.handler.EchoServerHandler;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
if(args.length!=1) {
System.err.println("Usage: "+EchoServer.class.getSimpleName()+ " <port>");
return;
}
new EchoServer(Integer.parseInt(args[0])).start();
}
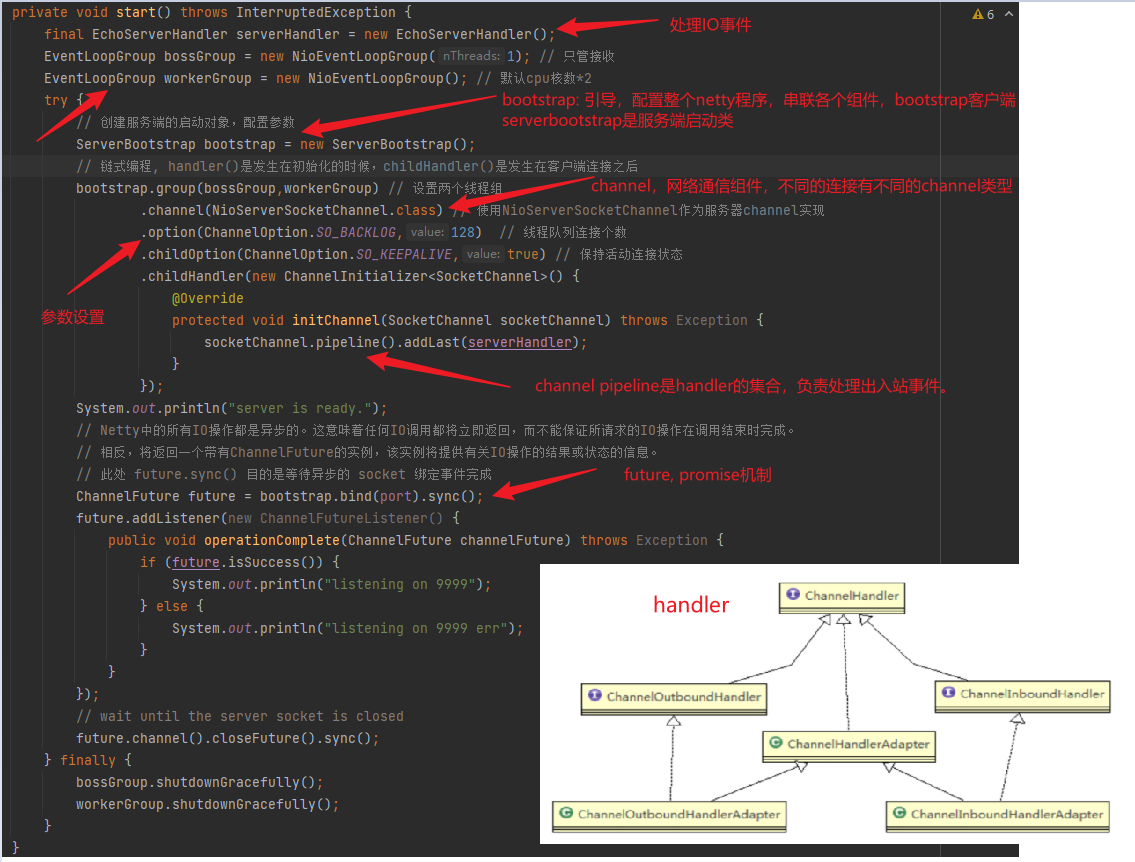
private void start() throws InterruptedException {
final EchoServerHandler serverHandler = new EchoServerHandler();
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // 只管接收
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 默认cpu核数*2
try {
// 创建服务端的启动对象,配置参数
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// 链式编程
//handler()是发生在初始化的时候,childHandler()是发生在客户端连接之后
bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup) // 设置两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 使用NioServerSocketChannel作为服务器channel实现
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128) // 线程队列连接个数
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true) // 保持活动连接状态
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(serverHandler);
}
});
System.out.println("server is ready.");
// 绑定端口并同步
// Netty中的所有IO操作都是异步的。这意味着任何IO调用都将立即返回,而不能保证所请求的IO操作在调用结束时完成。
// 相反,将返回一个带有ChannelFuture的实例,该实例将提供有关IO操作的结果或状态的信息。
// 此处 future.sync() 目的是等待异步的 socket 绑定事件完成
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("listening on 9999");
} else {
System.out.println("listening on 9999 err");
}
}
});
// wait until the server socket is closed
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
Bootstrap:提供了一个用于应用程序网络层配置的容器。
Channel:提供读、写、连接、绑定等的接口。
ChannelHandler:用于数据处理。常用ChannelInboundHandler,收到入站事件后处理应用逻辑。业务逻辑经常放在一个或者多个 ChannelInboundHandler。
ChannelPipeline:每个Channel都有自己的pipeline,在Channel创建时自动创建。
EchoClientHandler:
package cn.orzlinux.server.handler;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
// inbound入境
// 处理入站事件
@ChannelHandler.Sharable // 只是标识,标识这类的实例之间可以在channel里共享
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// 每个信息入站都会调用
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务端读取线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" channel="+ctx.channel());
System.out.println("server ctx = "+ctx);
System.out.println("看看channel 和 pipeline的关系");
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline(); //本质是一个双向链接, 出站入站
System.out.println("pipeline="+pipeline.toString());
//将 msg 转成一个 ByteBuf
//ByteBuf 是 Netty 提供的,不是 NIO 的 ByteBuffer.
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("客户端发送消息是:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("客户端地址:" + channel.remoteAddress());
}
// channel 最后一条消息调用
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 将数据写入缓存并刷新
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello, client!",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
// 读操作捕获异常时调用
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 打印堆栈异常
cause.printStackTrace();
// 关闭通道
ctx.close();
}
}
EchoClient.java
package cn.orzlinux.client;
import cn.orzlinux.client.handler.EchoClientHandler;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.Channel;
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public EchoClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
if(args.length!=2) {
System.err.println("Usage: "+EchoClient.class.getSimpleName()+ " <host> <port>");
return;
}
new EchoClient(args[0],Integer.parseInt(args[1])).start();
}
private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}
EchoClientHandler.java
package cn.orzlinux.client.handler;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler.Sharable;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
//标识同一个ChannelHandler的实例可以被多次添加到多个ChannelPipelines中,而且不会出现竞争条件。
@Sharable
public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
@Override
// 从服务器接收到数据后调用
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Client received: "+byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
// 服务器的连接被建立之后调用
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty rocks!",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
server输出:

任务队列
提交任务,或自定义,或定时,异步执行。
EchoServerHandler.java
package cn.orzlinux.server.handler;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
// inbound入境
// 处理入站事件
@ChannelHandler.Sharable // 只是标识,标识这类的实例之间可以在channel里共享
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// 每个信息入站都会调用
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
// 用户自定义任务
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("start sleep 5s",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
Thread.sleep(5*1000);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("sleep 5s done.......",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("channel code = "+ctx.channel().hashCode());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(() -> {
try {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("start sleep 10s",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
Thread.sleep(10*1000);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("sleep 10s done.........",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("channel code = "+ctx.channel().hashCode());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 用户自定义定时任务
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("sleep 20s done",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("channel code = "+ctx.channel().hashCode());
}
},20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
// channel 最后一条消息调用
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 将数据写入缓存并刷新
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello, client!",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
// 读操作捕获异常时调用
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 打印堆栈异常
cause.printStackTrace();
// 关闭通道
ctx.close();
}
}
http示例
HttpServer.java
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import java.net.URI;
public class MyHttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("对应的channel=" + ctx.channel() + " pipeline=" + ctx
.pipeline() + " 通过pipeline获取channel" + ctx.pipeline().channel());
System.out.println("当前ctx的handler=" + ctx.handler());
//判断 msg 是不是 httprequest请求
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
System.out.println("ctx 类型=" + ctx.getClass());
System.out.println("pipeline hashcode" + ctx.pipeline().hashCode() + " TestHttpServerHandler hash=" + this.hashCode());
System.out.println("msg 类型=" + msg.getClass());
System.out.println("客户端地址" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
//获取到
HttpRequest httpRequest = (HttpRequest) msg;
//获取uri, 过滤指定的资源
URI uri = new URI(httpRequest.uri());
if ("/favicon.ico".equals(uri.getPath())) {
System.out.println("请求了 favicon.ico, 不做响应");
return;
}
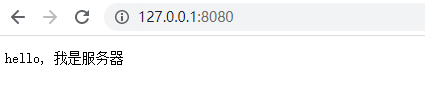
//回复信息给浏览器 [http协议]
ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, 我是服务器", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
//构造一个http的相应,即 httpresponse
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, content);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, content.readableBytes());
//将构建好 response返回
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}
MyHttpServerHandler.java
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import java.net.URI;
public class MyHttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("对应的channel=" + ctx.channel() + " pipeline=" + ctx
.pipeline() + " 通过pipeline获取channel" + ctx.pipeline().channel());
System.out.println("当前ctx的handler=" + ctx.handler());
//判断 msg 是不是 httprequest请求
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
System.out.println("ctx 类型=" + ctx.getClass());
System.out.println("pipeline hashcode" + ctx.pipeline().hashCode() + " TestHttpServerHandler hash=" + this.hashCode());
System.out.println("msg 类型=" + msg.getClass());
System.out.println("客户端地址" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
//获取到
HttpRequest httpRequest = (HttpRequest) msg;
//获取uri, 过滤指定的资源
URI uri = new URI(httpRequest.uri());
if ("/favicon.ico".equals(uri.getPath())) {
System.out.println("请求了 favicon.ico, 不做响应");
return;
}
//回复信息给浏览器 [http协议]
ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, 我是服务器", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
//构造一个http的相应,即 httpresponse
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, content);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, content.readableBytes());
//将构建好 response返回
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}
输出:
Netty核心模块组件
Unpooled:专门操作缓冲区的工具类。常用copiedBuffer,返回Bytebuf,类似NIO的Bytebuf。
WebSocket服务器和客户端长连接
http协议无状态,浏览器和服务器请求响应一次,下一次重新创建连接。转出websocket协议。
server:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler;
public class LongHttp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
// 以块方式写
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
// http在传输过程中分段,这里聚合多个段
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
//WebSocketServerProtocolHandler将http协议升级为ws协议,保持长连接
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/hello2"));
//自定义的handler ,处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new MyTextWebSocketFrameHandler());
}
});
//启动服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
handler:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class MyTextWebSocketFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务器收到消息 " + msg.text());
//回复消息
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("服务器时间" + LocalDateTime.now() + " " + msg.text()));
}
//当web客户端连接后, 触发方法
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handlerRemoved 被调用" + ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("异常发生 " + cause.getMessage());
ctx.close(); //关闭连接
}
}
测试:
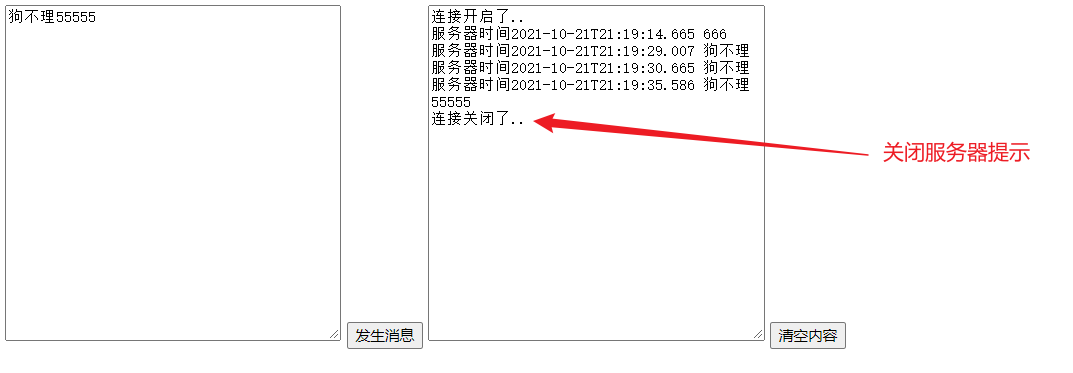
具体websocket可以看这篇文章。
Google Protobuf
netty自身提供了一些编解码器codec,但是底层还是用的Java序列化结束,效率低,且无法跨语言。google protobuf up。
TCP粘包拆包问题
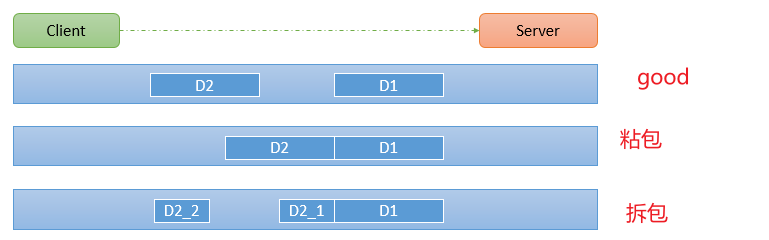
粘包原因
发送方原因
TCP默认使用Nagle算法(主要作用:减少网络中报文段的数量),而Nagle算法主要做两件事:只有上一个分组得到确认,才会发送下一个分组,收集多个小分组,在一个确认到来时一起发送。Nagle算法造成了发送方可能会出现粘包问题。
接收方原因
TCP接收到数据包时,并不会马上交到应用层进行处理,或者说应用层并不会立即处理。实际上,TCP将接收到的数据包保存在接收缓存里,然后应用程序主动从缓存读取收到的分组。这样一来,如果TCP接收数据包到缓存的速度大于应用程序从缓存中读取数据包的速度,多个包就会被缓存,应用程序就有可能读取到多个首尾相接粘到一起的包。
何时无需处理
连续数据流不需要处理,如在线视频。
每一个消息一次连接的情况,不需要处理。
UDP不需要处理。等等。
解决
使用自定义协议和编解码器解决。关键解决服务端每次读取数据长度问题。