几道力扣周赛题
Thread Runnable区别
Thread
public class Solution extends Thread {
String str;
Solution(String s) {
str = s;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(str);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Solution("A").start();
}
}
继承Thread方式
- 优点:编写简单,如果要访问当前线程,无需
Thread.currentThread()方法,直接this即可获得当前线程。 - 缺点:线程类继承了
Thread类,无法继承其他父类。
Runnable
public class Solution implements Runnable {
String str;
Solution(String s) {
str = s;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(str);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Solution("A")).start();
}
}
实现Runnable接口方式
- 优点:只是实现了接口,还可以继承其他类。多个线程可以共享一个目标对象,非常适合多个相同线程处理一份资源的情况,可以将CPU代码和数据分开,形成清晰的模型,较好体现面向对象的思想。
- 缺点:编程稍微复杂,如果要访问当前线程,需
Thread.currentThread()方法。
多线程按序打印:
实现一个多线程类,并用该线程类实例化3个线程A,B,C;A线程打印字符A,B线程打印字符B,C线程打印字符C;启动这3个线程,要求启动线程的顺序为C线程->B线程->A线程,并且最后输出内容为:
A
B
C
不能用sleep函数,注意考虑线程安全问题。
package cn.orzlinux;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
class MyThread extends Thread {
String str;
Semaphore before;
Semaphore after;
public MyThread(String s, Semaphore sem1,Semaphore sem2) {
before = sem1;
after = sem2;
str = s;
}
public void run() {
try {
before.acquire();
System.out.println(str);
after.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore sa = new Semaphore(1);
Semaphore sb = new Semaphore(0);
Semaphore sc = new Semaphore(0);
Thread a = new MyThread("A",sa,sb);
Thread b = new MyThread("B",sb,sc);
Thread c = new MyThread("C",sc,sa);
c.start();
b.start();
a.start();
}
}
169. 多数元素
摩尔投票法。
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
//if(nums.length==0) return -1;
int candidate = nums[0];
int vote = 1;
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++) {
if(nums[i]==candidate) {
vote++;
} else {
vote--;
if(vote==0) {
candidate = nums[i];
vote++;
}
}
}
return candidate;
}
}
使用「摩尔投票」的标准做法,在遍历数组时同时 check 这 k - 1个数,假设当前遍历到的元素为 x:
- 如果 x 本身是候选者的话,则对其出现次数加一;
- 如果 x 本身不是候选者,检查是否有候选者的出现次数为 00:
- 若有,则让 x 代替其成为候选者,并记录出现次数为 1;
- 若无,则让所有候选者的出现次数减一。
当处理完整个数组后,这 k - 1 个数可能会被填满,但不一定都是符合出现次数超过 n / k要求的。需要进行二次遍历,来确定候选者是否符合要求,将符合要求的数加到答案。
上述做法正确性的关键是:若存在出现次数超过 n / k的数,最后必然会成为这 k - 1 个候选者之一。
229. 求众数 II
class Solution {
public List<Integer> majorityElement(int[] nums) {
//超过n/3的最多有2个
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
int n = nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
if(countB!=0&& nums[i]==b) {
countB++;
} else if(countA!=0&& nums[i]==a) {
countA++;
} else if(countA==0) {
countA=1;
a = nums[i];
} else if(countB==0) {
countB=1;
b = nums[i];
} else {
countA--;
countB--;
}
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
countA = 0;
countB = 0;
for(int num:nums) {
if(num==a) countA++;
else if(num==b) countB++;
}
if(countA>n/3) list.add(a);
if(countB>n/3) list.add(b);
return list;
}
}
2135. 统计追加字母可以获得的单词数
位运算,可以再看一遍。
class Solution {
public int wordCount(String[] startWords, String[] targetWords) {
int mask = 0;
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for(String sw:startWords) {
mask = 0;
for(int i=0;i<sw.length();i++) {
mask |= 1<<(sw.charAt(i)-'a');
}
set.add(mask);
}
//System.out.println(set);
int result = 0;
for(String tw:targetWords) {
mask = 0;
for(int i=0;i<tw.length();i++) {
mask |= 1<<(tw.charAt(i)-'a');
}
int cur;
for(int i=0;i<tw.length();i++) {
cur = mask ^ 1<<(tw.charAt(i)-'a');
if(set.contains(cur)) {
result++;
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2134. 最少交换次数来组合所有的 1 II
没想起来思路,滑窗判断0的最小数。
class Solution {
public int minSwaps(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int windowSize = 0;
for(int num:nums) {
if(num==1) windowSize++;
}
if(windowSize==1) return 0;
int right = 0;
int left = (right+n-windowSize+1)%n;
int curOnes = nums[0];
for(int i=left;i<n;i++) {
curOnes+=nums[i];
}
int maxOnes = curOnes;
for(int i=right+1;i<n;i++) {
curOnes-=nums[left];
left = (i+n-windowSize+1)%n;
curOnes+=nums[i];
maxOnes = Math.max(maxOnes,curOnes);
}
return windowSize-maxOnes;
}
}
2136. 全部开花的最早一天
错误答法:
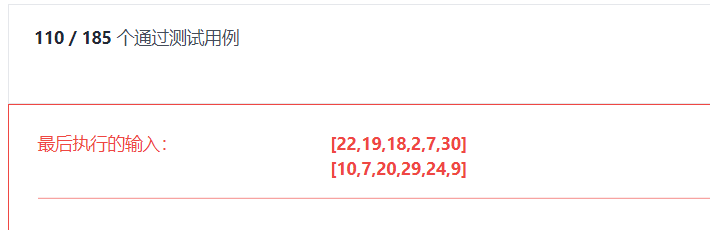
class Solution {
class Node {
double v;
int i;
public Node(double v,int i) {
this.v = v;
this.i = i;
}
}
public int earliestFullBloom(int[] plantTime, int[] growTime) {
int n = plantTime.length;
Node[] value = new Node[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
value[i]=new Node((0.0f+plantTime[i])/growTime[i],i);
}
Arrays.sort(value,(o1,o2)->o1.v-o2.v>0?1:-1);
int day = 0;
int cur = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int plant=value[i].i;
cur+=plantTime[plant];
day = Math.max(day,cur+growTime[plant]);
}
return day;
}
}