go进阶-上下文
上下文(Context)在1.7版本引入新标准库context,主要作用是在goroutine中进行上下文的传递,在传递信息中又包含了goroutine的运行控制、上下文信息传递等功能。
什么是context
会跨协程进行传播:
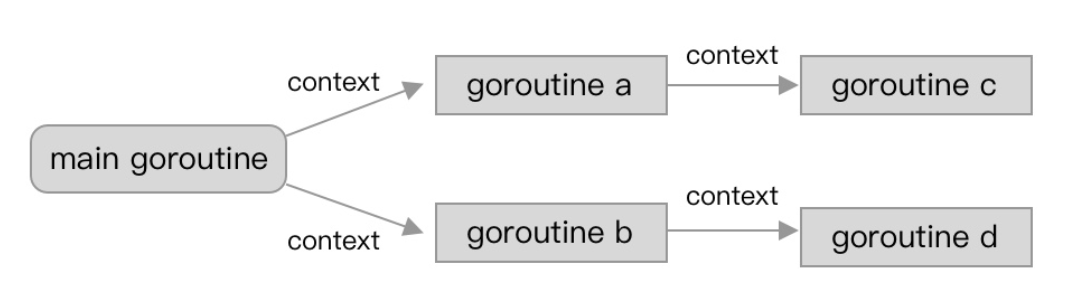
Go 就是基于 context 来实现和搭建各类协程控制,和select-case联合,实现上下文的截止时间,信号控制,信息传递等跨协程的操作,比较重要。
基本特性
demo:
func main() {
parentCtx := context.Background()
// context deadline exceeded
// ctx, cf := context.WithTimeout(parentCtx, 1*time.Millisecond)
// overslept
ctx, cf := context.WithTimeout(parentCtx, 3*time.Second)
defer cf()
select {
case <-time.After(time.Second):
fmt.Println("overslept")
case <-ctx.Done():
fmt.Println(ctx.Err())
}
}
context 其它方法:
// 创建一个可以取消的新context
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc)
// 创建一个具有截止时间戳的新context
func WithDeadline(parent Context, d time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc)
// 创建一个具有超时时间的context
func WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration) (Context, CancelFunc)
type Context
// 创建一个空context,一般用作根的父级context
func Background() Context
// 创建一个空的context,用于未确定时的声明信息
func TODO() Context
// 基于context创建并且存储上下文信息
func WithValue(parent Context, key, val interface{}) Context
context用法
withCancel demo:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
gen := func(ctx context.Context) <-chan int {
dst := make(chan int)
n := 1
go func() {
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return
case dst <- n:
n++
}
}
}()
return dst
}
ctx, cf := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
// 不被读掉的话,就会阻塞,生成器
for n := range gen(ctx) {
fmt.Println(n)
if n == 5 {
cf()
break
}
}
}
withValue demo:
func main() {
type key string
f := func(ctx context.Context, k key) {
if v := ctx.Value(k); v != nil {
fmt.Printf("v: %v\n", v)
return
}
fmt.Printf("key not found: %v\n", k)
}
k := key("lang")
ctx := context.WithValue(context.Background(), k, "go")
f(ctx, k)
f(ctx, key("haha"))
//v: go
//key not found: haha
}
context本质
如:
func WithDeadline(parent Context, d time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc)
返回的是一个新的上下文和取消函数。
context接口
Context:
type Context interface {
// 截止时间
Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool)
// 获取一个只读的channel,用于识别channel是否已经被关闭
Done() <-chan struct{}
// 获取当前
Err() error
// 获取当前context对应的上下文信息
// type any = interface{}
Value(key any) any
}
canceler接口:
type canceler interface {
cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error)
Done() <-chan struct{}
}
基础结构
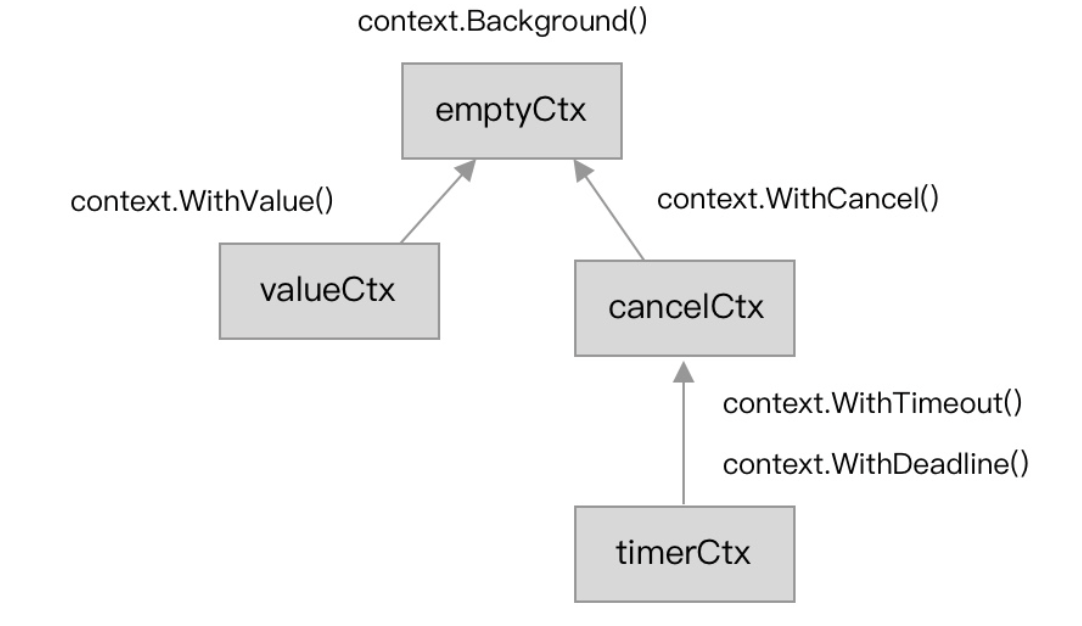
emptyCtx
var (
background = new(emptyCtx)
todo = new(emptyCtx)
)
// Background returns a non-nil, empty Context. It is never canceled, has no
// values, and has no deadline. It is typically used by the main function,
// initialization, and tests, and as the top-level Context for incoming
// requests.
func Background() Context {
return background
}
// TODO returns a non-nil, empty Context. Code should use context.TODO when
// it's unclear which Context to use or it is not yet available (because the
// surrounding function has not yet been extended to accept a Context
// parameter).
func TODO() Context {
return todo
}
它两个本质上都是emptyCtx的封装,emptyCtx如下:
// An emptyCtx is never canceled, has no values, and has no deadline. It is not
// struct{}, since vars of this type must have distinct addresses.
type emptyCtx int
func (*emptyCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {
return
}
func (*emptyCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
return nil
}
func (*emptyCtx) Err() error {
return nil
}
func (*emptyCtx) Value(key any) any {
return nil
}
只是个空定义。
cancelCtx
type CancelFunc func()
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) {
if parent == nil {
panic("cannot create context from nil parent")
}
c := newCancelCtx(parent)
// propagateCancel arranges for child to be canceled when parent is.
propagateCancel(parent, &c)
return &c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}
// newCancelCtx returns an initialized cancelCtx.
func newCancelCtx(parent Context) cancelCtx {
return cancelCtx{Context: parent}
}
还是比较清楚地,其中,cancel可以传递:
cancelCtx:
type cancelCtx struct {
Context // 匿名接口,实例化的时候也是要context的
mu sync.Mutex // protects following fields
done atomic.Value // of chan struct{}, created lazily, closed by first cancel call
// 所有子集context
children map[canceler]struct{} // set to nil by the first cancel call
err error // set to non-nil by the first cancel call
}
几个函数:
func (c *cancelCtx) Value(key any) any {
if key == &cancelCtxKey {
return c
}
return value(c.Context, key)
}
// 层层读取,见下文
func value(c Context, key any) any {
for {
switch ctx := c.(type) {
case *valueCtx:
if key == ctx.key {
return ctx.val
}
c = ctx.Context
case *cancelCtx:
if key == &cancelCtxKey {
return c
}
c = ctx.Context
case *timerCtx:
if key == &cancelCtxKey {
return &ctx.cancelCtx
}
c = ctx.Context
case *emptyCtx:
return nil
default:
return c.Value(key)
}
}
}
func (c *cancelCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
d := c.done.Load()
if d != nil {
return d.(chan struct{})
}
c.mu.Lock()
defer c.mu.Unlock()
d = c.done.Load()
if d == nil {
d = make(chan struct{})
c.done.Store(d)
}
return d.(chan struct{})
}
func (c *cancelCtx) Err() error {
c.mu.Lock()
err := c.err
c.mu.Unlock()
return err
}
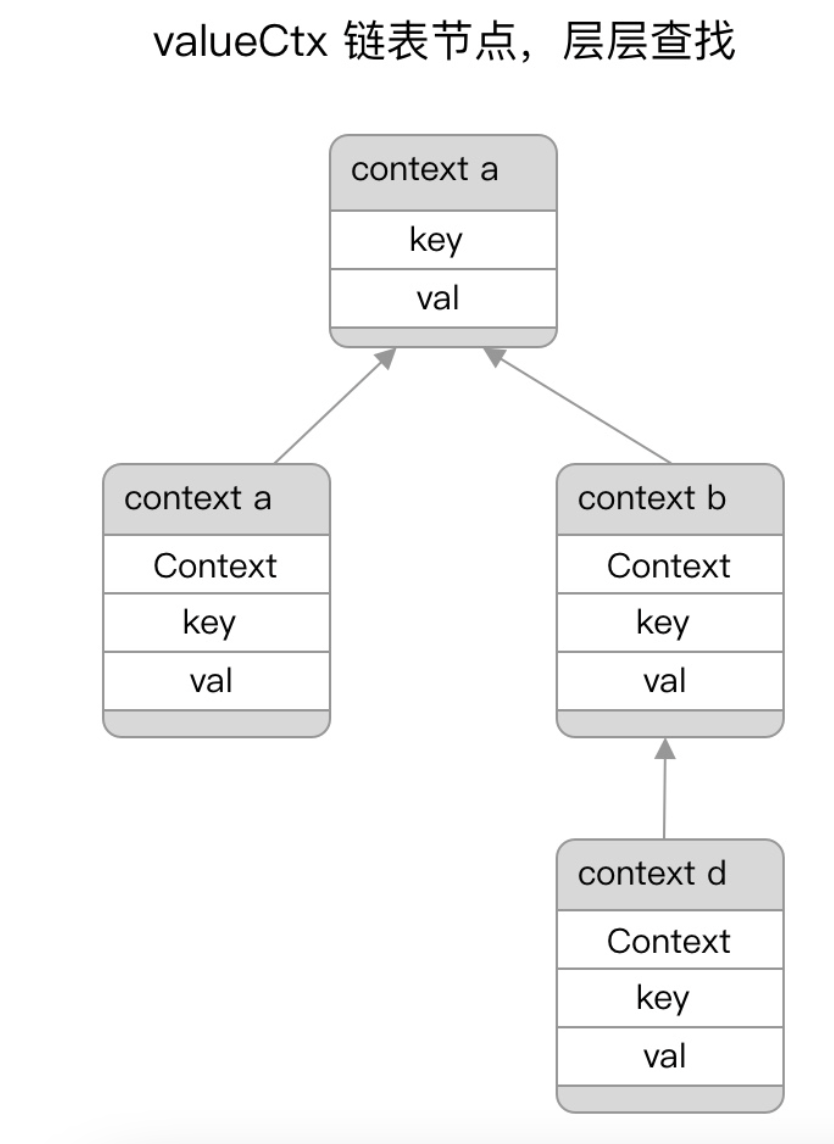
其它的类似,用到再说。