6.824分布式lab1-MapReduce通过
任务
Distributed MapReduce。详见:mit 6.824 lab1
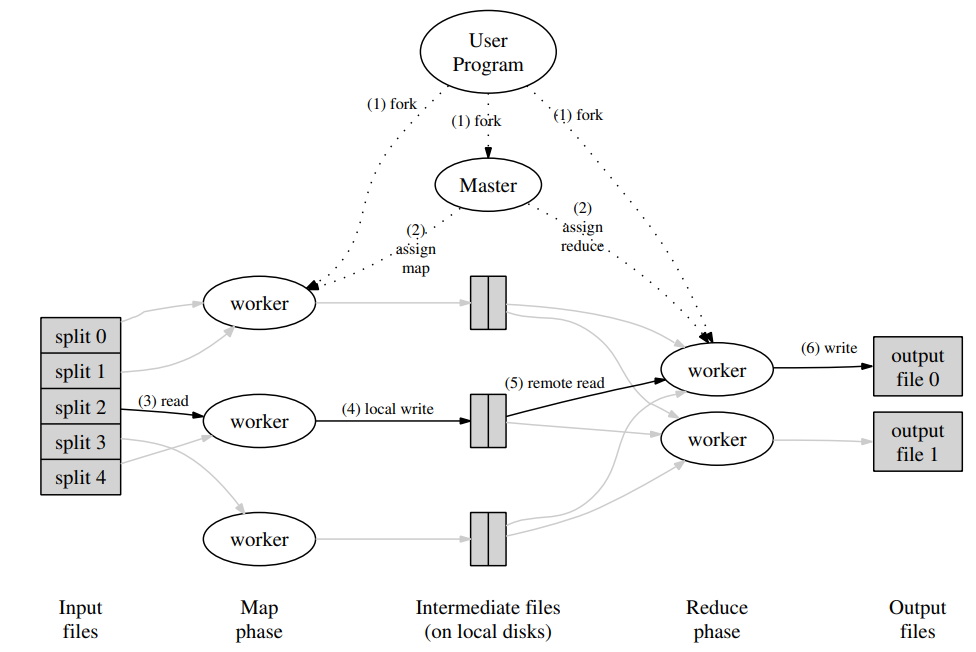
process分为两个:coordinator(协调者)和worker process。coordinator只有一个,worker可以有一个或者多个,并行执行。实际场景worker应该在不同的机器上运行,这里只是跑在单机上来测试。通过RPC通信。worker process向coordinator索要任务,读取任务的输入,然后执行,将任务结果写入文件。如果 worker在一定时间内没有完成任务(如10s),coordinator 应该把这些任务分派给别的worker。
MapReduce
RPC
首先要解决的是通信的问题。
demo
server.go
package main
import (
"errors"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"net/rpc"
)
type RpcRequest struct {
A, B int
}
type RpcResponse struct {
Quo, Rem int
}
type SomeType int
func (t *SomeType) Multiply(req *RpcRequest, response *int) error {
*response = req.A * req.B
return nil
}
func (t *SomeType) Divide(req *RpcRequest, response *RpcResponse) error {
if req.B == 0 {
return errors.New("divided by 0")
}
response.Quo = req.A / req.B
response.Rem = req.A % req.B
return nil
}
func main() {
st := new(SomeType)
// 注册rpc服务
rpc.Register(st)
// rpc服务挂载到http服务上
rpc.HandleHTTP()
l, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("listen error: ", err)
}
// http服务打开后就可通过rpc客户端调用方法
http.Serve(l, nil)
}
client.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/rpc"
)
// 参数定义都需要的
type RpcRequest struct {
A, B int
}
type RpcResponse struct {
Quo, Rem int
}
func main() {
c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1:1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("dialing: ", err)
}
// 同步调用,等待请求结束
req := &RpcRequest{9, 4}
var reply int
c.Call("SomeType.Multiply", req, &reply)
fmt.Printf("reply: %v\n", reply)
// 异步调用,返回一个channel
response := new(RpcResponse)
c2 := c.Go("SomeType.Divide", req, &response, nil)
fmt.Println("do something else")
<-c2.Done
fmt.Printf("response: %v\n", response)
// output
// reply: 36
// do something else
// response: &{2 1}
}
疑问
要写入三个文件,一个coordinator,一个worker,一个rpc,但是work怎么区分map和reduce?
看下主函数:mrcoordinator和mrworker。
mrcoordinator.go
func main() {
if len(os.Args) < 2 {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "Usage: mrcoordinator inputfiles...\n")
os.Exit(1)
}
m := mr.MakeCoordinator(os.Args[1:], 10)
for m.Done() == false {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
只是单纯调用,然后等待结束。
mrworker.go
func main() {
if len(os.Args) != 2 {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "Usage: mrworker xxx.so\n")
os.Exit(1)
}
mapf, reducef := loadPlugin(os.Args[1])
mr.Worker(mapf, reducef)
}
//
// load the application Map and Reduce functions
// from a plugin file, e.g. ../mrapps/wc.so
//
func loadPlugin(filename string) (func(string, string) []mr.KeyValue, func(string, []string) string) {
p, err := plugin.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot load plugin %v", filename)
}
xmapf, err := p.Lookup("Map")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot find Map in %v", filename)
}
mapf := xmapf.(func(string, string) []mr.KeyValue)
xreducef, err := p.Lookup("Reduce")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot find Reduce in %v", filename)
}
reducef := xreducef.(func(string, []string) string)
return mapf, reducef
}
OK,这个也是加载插件后,调用Worker,这尼玛还得在自己写的worker下面实现。
好家伙,测试文件也没有说咋区分负责map的worker和负责reduce的worker:
# first word-count
# generate the correct output
../mrsequential ../../mrapps/wc.so ../pg*txt || exit 1
sort mr-out-0 > mr-correct-wc.txt
rm -f mr-out*
echo '***' Starting wc test.
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrcoordinator ../pg*txt &
pid=$!
# give the coordinator time to create the sockets.
sleep 1
# start multiple workers.
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrworker ../../mrapps/wc.so &
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrworker ../../mrapps/wc.so &
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrworker ../../mrapps/wc.so &
# wait for the coordinator to exit.
wait $pid
# since workers are required to exit when a job is completely finished,
# and not before, that means the job has finished.
sort mr-out* | grep . > mr-wc-all
if cmp mr-wc-all mr-correct-wc.txt
then
echo '---' wc test: PASS
else
echo '---' wc output is not the same as mr-correct-wc.txt
echo '---' wc test: FAIL
failed_any=1
fi
冒出来一个思路,先去尝试reduce,如果中间文件都经过reduce了,那就去map。
具体咋样再说,之后再看别人咋实现的,先能跑再说。
~worker请求coordinator一个中间文件,参数无,返回string类型文件名。如果正经文件就reduce,否则就请求map,参数无,返回值一个未处理过的文件名,将数据写入中间文件,然后发送给coordinator一个处理完成的信号(rpc访问某个函数),同样不需要参数。但是需要将不同的worker区分开,就搞一个随机字符串作为输入参数。~~
改:还是全部map,然后全部reduce。
version 0.1
错误版本,想法:coordinator作为协调者。worker启动之后,先向coordinator请求一个初始的要计数文件。然后读取文件内容,交给map得到【单词:1】这样的序列,并记录为中间文件。如果worker map之前的请求返回了'done',也就是已经全部处理为了中间文件,就接着reduce前的操作,就是利用分档的思想,将其中一个中间文件排序,相同的交给reduce,然后记录最终文件。循环直至全部处理结束。
rpc.go
package mr
//
// RPC definitions.
//
// remember to capitalize all names.
//
import (
"os"
"strconv"
)
type MapRequest struct {
Uid string
}
type MapResponse struct {
Filename string
State string
}
type MapTaskState struct {
Filename string
State string
}
type ReduceRequest struct {
Uid string
}
type ReduceResponse struct {
Filename string
State string
}
type ReduceTaskState struct {
Filename string
OutFilename string
State string
}
coordinator.go
package mr
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"net/rpc"
"strings"
"sync"
)
var void interface{}
type Coordinator struct {
// filename list
files []string
reduceId int //分配给worker的id号
midFiles []string
// 通过rpc发送了,但是还没有收到完成信号的
mapSend map[string]interface{}
reduceSend map[string]interface{}
nReduce int
ok bool // 任务是否完毕
// 保护files
mtx sync.Mutex
}
func (c *Coordinator) GetWorkerId(i, j *int) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
*j = c.reduceId
c.reduceId++
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
// map调用,返回第一个文件名
func (c *Coordinator) GetInputFile(req *MapRequest, resp *MapResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.files) == 0 {
resp.Filename = ""
if len(c.mapSend) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
}
} else {
resp.Filename = c.files[0]
c.files = c.files[1:]
c.mapSend[resp.Filename] = void
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
// fmt.Printf("c.files: %v\n", c.files)
return nil
}
// reduce之前,返回中间文件的文件名
func (c *Coordinator) GetMapOutFile(req *ReduceRequest, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.midFiles) == 0 {
resp.Filename = ""
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 && len(c.midFiles) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
}
} else {
resp.Filename = c.midFiles[0]
c.midFiles = c.midFiles[1:]
c.reduceSend[resp.Filename] = void
}
// fmt.Printf("c.midFiles: %v\n", c.midFiles)
// fmt.Printf("c.reduceSend: %v\n", c.reduceSend)
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
// map处理完毕了调用,防止某一个处理过程中崩溃,如果彻底崩溃了,设置10s超时,再把这个
// 元素加回去, 全部文件结束了之后,得到全部的中间文件名list。
func (c *Coordinator) MapInputFileResp(state *MapTaskState, resp *MapResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
// fmt.Printf("state: %v\n", state)
if state.State == "done" {
// ok了,删除这个元素
names := strings.Split(state.Filename, "+")
delete(c.mapSend, names[1])
c.midFiles = append(c.midFiles, names[0])
// fmt.Printf("names[0]: %v\n", names[0])
} else {
// 处理没成功,重新处理
c.files = append(c.files, state.Filename)
// 不删除,这样状态一直存在,知道再次被分配了,然后delete
// delete(c.mapSend, state.filename)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
// fmt.Printf("c.files: %v\n", c.files)
return nil
}
func (c *Coordinator) ReduceStateResp(state *ReduceTaskState, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
// fmt.Printf("state: %v\n", state)
if state.State == "done" {
// ok了,删除这个元素
delete(c.reduceSend, state.Filename)
// fmt.Printf("c.reduceSend: %v\n", c.reduceSend)
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 && len(c.midFiles) == 0 {
c.ok = true
}
} else {
// 处理没成功,重新处理
c.midFiles = append(c.midFiles, state.Filename)
// 不删除,这样状态一直存在,知道再次被分配了,然后delete
// delete(c.mapSend, state.filename)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
// fmt.Printf("c.midfiles: %v\n", c.midFiles)
return nil
}
func dicheck(c *Coordinator, filename string) {
panic("unimplemented")
}
//
// start a thread that listens for RPCs from worker.go
//
func (c *Coordinator) server() {
rpc.Register(c)
rpc.HandleHTTP()
l, e := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
// sockname := coordinatorSock()
// os.Remove(sockname)
// l, e := net.Listen("unix", sockname)
if e != nil {
log.Fatal("listen error:", e)
}
go http.Serve(l, nil)
}
//
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls Done() periodically to find out
// if the entire job has finished.
//
func (c *Coordinator) Done() bool {
c.mtx.Lock()
ret := c.ok
c.mtx.Unlock()
// Your code here.
return ret
}
//
// create a Coordinator.
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls this function.
// nReduce is the number of reduce tasks to use.
//
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {
c := Coordinator{}
// Your code here.
c.nReduce = nReduce
c.files = files
c.midFiles = []string{}
c.mtx = sync.Mutex{}
c.mapSend = make(map[string]interface{})
c.reduceSend = make(map[string]interface{})
c.server()
fmt.Printf("c: %v\n", c)
return &c
}
worker.go
package mr
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"hash/fnv"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/rpc"
"os"
"sort"
"strconv"
"time"
)
//
// Map functions return a slice of KeyValue.
//
type KeyValue struct {
Key string
Value string
}
//
// use ihash(key) % NReduce to choose the reduce
// task number for each KeyValue emitted by Map.
//
func ihash(key string) int {
h := fnv.New32a()
h.Write([]byte(key))
return int(h.Sum32() & 0x7fffffff)
}
func getMapMidFile(workerId int, mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue, c *rpc.Client) {
// 先尝试一直map,获取文件名,生成中间文件。
retryTimes := 0
mapCount := 0
s_id := strconv.Itoa(workerId)
// fmt.Printf("s_id: %v\n", s_id)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
for retryTimes < 3 {
req := MapRequest{s_id}
resp := MapResponse{}
err2 := c.Call("Coordinator.GetInputFile", &req, &resp)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("err2: %v\n", err2)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
retryTimes++
continue
}
retryTimes = 0
if resp.State == "done" {
break
}
if resp.Filename == "" {
// 为空,但是没done,证明有问题了,等一秒重试
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
// 文件名获取没有问题
// deal with resp filename
// write to disk
req2 := MapTaskState{resp.Filename, "done"}
resp2 := MapResponse{}
f, err := os.Open(resp.Filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
req2.State = "nosuchfile"
c.Call("Coordinator.MapInputFileResp", &req2, &resp2)
continue
}
defer f.Close()
content, err := ioutil.ReadAll(f)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", resp.Filename)
req2.State = "filereaderr"
c.Call("Coordinator.MapInputFileResp", &req2, &resp2)
}
kvs := mapf(resp.Filename, string(content))
// fmt.Printf("uuid: %v\n", s_id)
outFilename := fmt.Sprintf("%s%s_%d", "mr-mid-", s_id, mapCount)
mapCount++
// fmt.Printf("outFilename: %v\n", outFilename)
out, _ := os.Create(outFilename)
defer out.Close()
enc := json.NewEncoder(out)
for _, kv := range kvs {
enc.Encode(kv)
}
req2.Filename = outFilename + "+" + resp.Filename
req2.State = "done"
err = c.Call("Coordinator.MapInputFileResp", &req2, &resp2)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err: %v\n", err)
}
// then send to MapInputFileResp
// fmt.Printf("resp: %v\n", resp)
}
}
func getReduceList(workerId int, reducef func(string, []string) string, client *rpc.Client) {
reduceCount := 0
// 服务器运行完关闭或者网络有问题,重试
// 几次后退出
retryTimes := 0
s_id := strconv.Itoa(workerId)
for retryTimes < 3 {
req := ReduceRequest{s_id}
var resp ReduceResponse
err2 := client.Call("Coordinator.GetMapOutFile", &req, &resp)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("err2: %v\n", err2)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
retryTimes++
continue
}
retryTimes = 0
if resp.State == "done" {
return
}
if len(resp.Filename) == 0 {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Println("job assign done. but others workers are running")
continue
}
// 至此,resp.Filename是中间文件的名字了
// 下一步,读取内容,排序,调用reduce。
// 类似串行的,只是这里是部分文件,传给
// coordinate之后再组合吧
req2 := ReduceTaskState{resp.Filename, "", ""}
resp2 := ReduceResponse{}
f, err := os.Open(resp.Filename)
// fmt.Printf("resp.Filename: %v\n", resp.Filename)
defer f.Close()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("mid file open wrong:", err)
req2.State = "nosuchfile"
client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
continue
}
d := json.NewDecoder(f)
kva := []KeyValue{}
jsonParseState := true
for {
var kv KeyValue
if err := d.Decode(&kv); err != nil {
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
fmt.Println("json parse:", err)
req2.State = "jsonparseerr"
client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
jsonParseState = false
break
}
// fmt.Printf("kv: %v\n", kv)
kva = append(kva, kv)
}
if jsonParseState {
sort.Sort(byKey(kva))
outFilename := fmt.Sprintf("%s%s_%d", "mr-out-", s_id, reduceCount)
reduceCount++
// fmt.Printf("outFilename: %v\n", outFilename)
out, _ := os.Create(outFilename)
defer out.Close()
i := 0
for i < len(kva) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(kva) && kva[i].Key == kva[j].Key {
j++
}
vv := []string{}
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
vv = append(vv, kva[k].Value)
}
s := reducef(kva[i].Key, vv)
fmt.Fprintf(out, "%v %v\n", kva[i].Key, s)
i = j
}
req2.State = "done"
req2.OutFilename = outFilename
client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
}
}
}
type byKey []KeyValue
func (a byKey) Len() int { return len(a) }
func (a byKey) Swap(i, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] }
func (a byKey) Less(i, j int) bool { return a[i].Key < a[j].Key }
//
// main/mrworker.go calls this function.
//
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,
reducef func(string, []string) string) {
// 定义一个uuid
i := 0
var workerId int
c, _ := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
defer c.Close()
c.Call("Coordinator.GetWorkerId", &i, &workerId)
// fmt.Printf("workerId: %v\n", workerId)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
getMapMidFile(workerId, mapf, c)
// 至此,mid中间文件全部生成,可向coordinate请求中间文件名
// 按照mrsequential的做法
// 接下来就是请求一个中间文件,排序,计数,发送给coordinate
getReduceList(workerId, reducef, c)
}
//
// example function to show how to make an RPC call to the coordinator.
//
// the RPC argument and reply types are defined in rpc.go.
//
func CallExample() {
// declare an argument structure.
args := ExampleArgs{}
// fill in the argument(s).
args.X = 99
// declare a reply structure.
reply := ExampleReply{}
// send the RPC request, wait for the reply.
call("Coordinator.Example", &args, &reply)
// reply.Y should be 100.
fmt.Printf("reply.Y %v\n", reply.Y)
}
//
// send an RPC request to the coordinator, wait for the response.
// usually returns true.
// returns false if something goes wrong.
//
func call(rpcname string, args interface{}, reply interface{}) bool {
c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
// sockname := coordinatorSock()
// c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("unix", sockname)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("dialing:", err)
}
defer c.Close()
err = c.Call(rpcname, args, reply)
if err == nil {
return true
}
fmt.Println(err)
return false
}
总结
目前只是放到了单个文件,还没组合,也没有考虑崩溃或者网络延时导致的任务重复执行问题。可能还有其他问题,先改着。
version 0.2
组合文件
直接返回给coordinator,让coordinator来组合。
问题:咋组合?直接排序吗?大文件咋搞?根据首字母再拆分成小文件放入内存中组合?数据库?
先直接全文件放入内存排序吧。
func (c *Coordinator) ReduceStateResp(state *ReduceTaskState, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
//...reduce之后发给coordinator的信号
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 && len(c.midFiles) == 0 && !c.ok {
// 组合
go func() {
c.mtx.Lock()
if c.ok {
c.mtx.Unlock()
return
}
combineReduceFiles()
c.ok = true
c.mtx.Unlock()
}()
}
// fmt.Printf("c.midfiles: %v\n", c.midFiles)
return nil
}
combineReduceFiles():
func combineReduceFiles() {
matches, _ := filepath.Glob("mr-reduceout*")
fmt.Println(matches)
allWords := make(map[string]int)
for _, midfile := range matches {
fmt.Println("dealing ", midfile, "....")
f, _ := os.Open(midfile)
fileScanner := bufio.NewScanner(f)
for fileScanner.Scan() {
s := strings.Split(fileScanner.Text(), " ")
_, ok := allWords[s[0]]
if !ok {
allWords[s[0]] = 0
}
wc, _ := strconv.Atoi(s[1])
allWords[s[0]] += wc
}
}
f, _ := os.Create("mr-out-X")
ks := make([]string, len(allWords))
i := 0
for k, _ := range allWords {
ks[i] = k
i++
}
sort.Strings(ks)
for _, k := range ks {
fmt.Fprintf(f, "%v %v\n", k, allWords[k])
// fmt.Printf("%v %v\n", k, allWords[k])
}
}
map 默认是无序的,不管是按照 key 还是按照 value 默认都不排序。
如果你想为 map 排序,需要将 key(或者 value)拷贝到一个切片,再对切片排序,然后可以使用切片的 for-range 方法打印出所有的 key 和 value。
测试方式:
一顿操作猛如虎,一看,只有正确性过了。
--- wc test: PASS
看下这段的逻辑:
../mrsequential ../../mrapps/wc.so ../pg*txt || exit 1
sort mr-out-0 > mr-correct-wc.txt
rm -f mr-out*
echo '***' Starting wc test.
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrcoordinator ../pg*txt &
pid=$!
# $! 获得之前(上一个)进程 ID
# give the coordinator time to create the sockets.
sleep 1
# start multiple workers.
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrworker ../../mrapps/wc.so &
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrworker ../../mrapps/wc.so &
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrworker ../../mrapps/wc.so &
# wait for the coordinator to exit.
wait $pid
# since workers are required to exit when a job is completely finished,
# and not before, that means the job has finished.
sort mr-out* | grep . > mr-wc-all
if cmp mr-wc-all mr-correct-wc.txt
then
echo '---' wc test: PASS
else
echo '---' wc output is not the same as mr-correct-wc.txt
echo '---' wc test: FAIL
failed_any=1
fi
下一个更改:
Starting indexer test
之前先看这个:
timeout -k 2s 180s ../mrworker ../../mrapps/wc.so &
代表:命令运行180s,如果到时间了没有结束,就在2s后终止。
indexer test
这个就是wc.so插件换成了indexer插件,里面是map函数和reduce函数,也就是功能不一样。
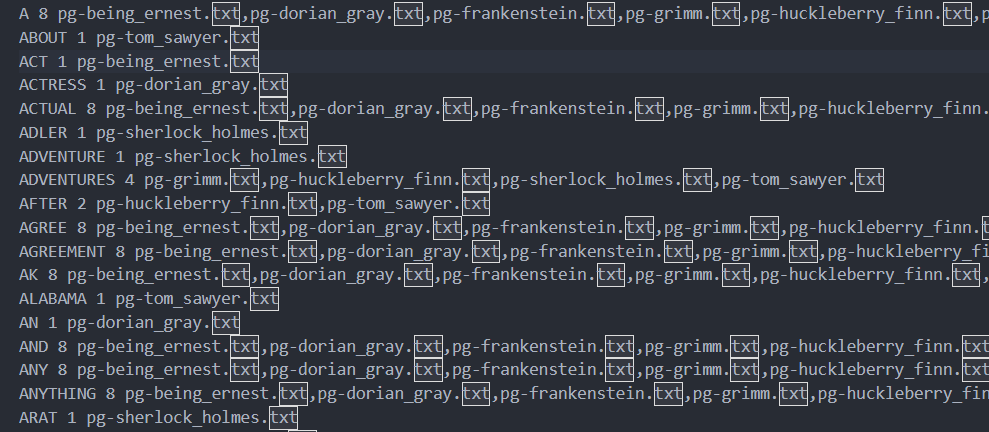
这个是要记录单词出现的问题。
出现问题了,我之前是分档的,reduce产生的文件要组合的,但是这种方式,我不知道coordinator要怎么协调。coordinator是没有插件的:
$ go run mrcoordinator.go p*.txt
要想reduce获取一个单词的全部value,需要全局信息,怎么搞?
看了几眼别人的代码,答案:保存的时候,用hash,同一个字符保存到一个文件里面。这样的话最后也不用组合了。
还是理解的有问题,应该是hash然后同一个键保存到同一个文件里的是map产生的文件,out还是可以一个worker一个。
里面又牵扯到崩溃保存的问题,如果是多个worker写同一个文件,其中一个崩了就没法恢复了。应该先写创建临时文件,确保执行完成了再重命名为mr-mid-{workid}-{nreduceid}。这样就算执行失败了或者重命名过程中执行失败了,存在的中间文件一定是对的,reduce时nreduceid号相同的是同一个文件。
临时文件使用如下:
f, _ := os.CreateTemp("./", "di-mp") fmt.Printf("f.Name(): %v\n", f.Name()) f.Close() fmt.Printf("f.Name(): %v\n", f.Name()) time.Sleep(time.Second * 5) os.Rename(f.Name(), "didit") // os.Remove(f.Name()) // f.Name(): C:\Users\PC\AppData\Local\Temp\di-mp2850179130 // f.Name(): C:\Users\PC\AppData\Local\Temp\di-mp2850179130
map之后reduce请求的时候应该给它所有同一个reduce的文件,才能保证out里一个文件里有同一个单词的所有东西。
小插曲:sort命令
我的sort命令默认没有按照它所说的:大小写敏感。百思不得其解,我也没有alias,但是就是没法用。
在网上找到了答案:
export LC_ALL=C
然后就可以了:
LC_ALL=C 是为了去除所有本地化的设置,让命令能正确执行。应该是默认sort使用的字符串比较方式在不同的语言下有区别。
代码
这次思路貌似大方向是对了。
rpc.go
package mr
//
// RPC definitions.
//
// remember to capitalize all names.
//
import (
"os"
"strconv"
)
//
// example to show how to declare the arguments
// and reply for an RPC.
//
type ExampleArgs struct {
X int
}
type ExampleReply struct {
Y int
}
// Add your RPC definitions here.
// Cook up a unique-ish UNIX-domain socket name
// in /var/tmp, for the coordinator.
// Can't use the current directory since
// Athena AFS doesn't support UNIX-domain sockets.
func coordinatorSock() string {
s := "/var/tmp/824-mr-"
s += strconv.Itoa(os.Getuid())
return s
}
// 不需要参数,要我就随机给一个文件
type MapRequest struct {
}
// 文件名和当前状态,应是有必要的
type MapResponse struct {
Filename string
State string
}
type MapTaskState struct {
Filename string
WorkerId int
TaskId int
State string
}
type ReduceRequest struct {
}
type ReduceResponse struct {
ReduceId int
Filenames []string
State string
}
type ReduceTaskState struct {
ReduceId int
State string
}
type WorkerInfo struct {
NReduce int
WorkId int
}
coordinator.go
package mr
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"net/rpc"
"sync"
)
var void interface{}
type stringArray []string
type Coordinator struct {
// filename list
files []string
reduceId int //分配给worker的id号
midFilesMap map[int]stringArray //reduceId:stringArray
midFilesList []int
// 通过rpc发送了,但是还没有收到完成信号的
mapSend map[string]interface{}
reduceSend map[int]interface{} //key: reduceId
nReduce int
ok bool // 任务是否完毕
// 保护files
mtx sync.Mutex
}
func (c *Coordinator) AssignWorkerId(i *int, wi *WorkerInfo) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
wi.WorkId = c.reduceId
wi.NReduce = c.nReduce
c.reduceId++
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
// Your code here -- RPC handlers for the worker to call.
//
// an example RPC handler.
//
// the RPC argument and reply types are defined in rpc.go.
//
func (c *Coordinator) Example(args *ExampleArgs, reply *ExampleReply) error {
reply.Y = args.X + 1
return nil
}
// map调用,返回第一个文件名
func (c *Coordinator) AssignMapTask(req *MapRequest, resp *MapResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.files) == 0 {
resp.Filename = ""
if len(c.mapSend) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
fmt.Println("map task done.")
}
} else {
resp.Filename = c.files[0]
c.files = c.files[1:]
c.mapSend[resp.Filename] = void
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
// fmt.Printf("c.files: %v\n", c.files)
fmt.Printf("c.files: %v\n", c.files)
fmt.Printf("c.mapSend: %v\n", c.mapSend)
return nil
}
// reduce之前,返回中间文件的文件名
func (c *Coordinator) AssignReduceTask(req *ReduceRequest, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.midFilesList) == 0 {
resp.Filenames = nil
resp.ReduceId = -1
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
fmt.Println("reduce task done")
}
} else {
resp.ReduceId = c.midFilesList[0]
c.midFilesList = c.midFilesList[1:]
resp.Filenames = c.midFilesMap[resp.ReduceId]
c.reduceSend[resp.ReduceId] = void
}
fmt.Printf("c.midFiles: %v\n", c.midFilesList)
fmt.Printf("c.reduceSend: %v\n", c.reduceSend)
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
// map处理完毕了调用,防止某一个处理过程中崩溃,如果彻底崩溃了,设置10s超时,再把这个
// 元素加回去, 全部文件结束了之后,得到全部的中间文件名list。
func (c *Coordinator) MapTaskResp(state *MapTaskState, resp *MapResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
// fmt.Printf("state: %v\n", state)
if state.State == "done" {
// ok了,删除这个元素
delete(c.mapSend, state.Filename)
for i := 0; i < c.nReduce; i++ {
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d-%d_%d", "mr-mid", state.WorkerId, state.TaskId, i)
_, ok := c.midFilesMap[i]
if !ok {
c.midFilesMap[i] = stringArray{}
}
c.midFilesMap[i] = append(c.midFilesMap[i], name)
}
// fmt.Printf("names[0]: %v\n", names[0])
} else {
// 处理没成功,重新处理
c.files = append(c.files, state.Filename)
// 不删除,这样状态一直存在,知道再次被分配了,然后delete
// delete(c.mapSend, state.filename)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
func (c *Coordinator) ReduceStateResp(state *ReduceTaskState, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
// fmt.Printf("state: %v\n", state)
if state.State == "done" {
// ok了,删除这个元素
delete(c.reduceSend, state.ReduceId)
// fmt.Printf("c.reduceSend: %v\n", c.reduceSend)
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 && len(c.midFilesList) == 0 && !c.ok {
c.ok = true
}
} else {
// 处理没成功,重新处理
c.midFilesList = append(c.midFilesList, state.ReduceId)
// 不删除,这样状态一直存在,知道再次被分配了,然后delete
// delete(c.mapSend, state.filename)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
// if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 && len(c.midFiles) == 0 && !c.ok {
// // 组合
// go func() {
// c.mtx.Lock()
// if c.ok {
// c.mtx.Unlock()
// return
// }
// combineReduceFiles()
// c.ok = true
// c.mtx.Unlock()
// }()
// }
// fmt.Printf("c.midfiles: %v\n", c.midFiles)
return nil
}
// func combineReduceFiles() {
// matches, _ := filepath.Glob("mr-reduceout*")
// fmt.Println(matches)
// allWords := make(map[string]int)
// for _, midfile := range matches {
// fmt.Println("dealing ", midfile, "....")
// f, _ := os.Open(midfile)
// fileScanner := bufio.NewScanner(f)
// for fileScanner.Scan() {
// s := strings.Split(fileScanner.Text(), " ")
// _, ok := allWords[s[0]]
// if !ok {
// allWords[s[0]] = 0
// }
// wc, _ := strconv.Atoi(s[1])
// allWords[s[0]] += wc
// }
// }
// f, _ := os.Create("mr-out-X")
// ks := make([]string, len(allWords))
// i := 0
// for k, _ := range allWords {
// ks[i] = k
// i++
// }
// sort.Strings(ks)
// for _, k := range ks {
// fmt.Fprintf(f, "%v %v\n", k, allWords[k])
// // fmt.Printf("%v %v\n", k, allWords[k])
// }
// }
//
// start a thread that listens for RPCs from worker.go
//
func (c *Coordinator) server() {
rpc.Register(c)
rpc.HandleHTTP()
l, e := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
// sockname := coordinatorSock()
// os.Remove(sockname)
// l, e := net.Listen("unix", sockname)
if e != nil {
log.Fatal("listen error:", e)
}
go http.Serve(l, nil)
}
//
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls Done() periodically to find out
// if the entire job has finished.
//
func (c *Coordinator) Done() bool {
c.mtx.Lock()
ret := c.ok
c.mtx.Unlock()
// Your code here.
return ret
}
//
// create a Coordinator.
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls this function.
// nReduce is the number of reduce tasks to use.
//
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {
c := Coordinator{}
// Your code here.
c.nReduce = nReduce
c.files = files
c.midFilesMap = map[int]stringArray{}
c.midFilesList = []int{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
c.mtx = sync.Mutex{}
c.mapSend = make(map[string]interface{})
c.reduceSend = make(map[int]interface{})
c.server()
fmt.Printf("c: %v\n", c)
return &c
}
worker.go
package mr
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"hash/fnv"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/rpc"
"os"
"sort"
"time"
)
//
// Map functions return a slice of KeyValue.
//
type KeyValue struct {
Key string
Value string
}
//
// use ihash(key) % NReduce to choose the reduce
// task number for each KeyValue emitted by Map.
//
func ihash(key string) int {
h := fnv.New32a()
h.Write([]byte(key))
return int(h.Sum32() & 0x7fffffff)
}
var workerInfo WorkerInfo
var midFiles []*os.File
func WorkerMap(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue, c *rpc.Client) {
// 先尝试一直map,获取文件名,生成中间文件。
retryTimes := 0
taskid := 0
for retryTimes < 3 {
req := MapRequest{}
resp := MapResponse{}
err2 := c.Call("Coordinator.AssignMapTask", &req, &resp)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("err2: %v\n", err2)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
retryTimes++
continue
}
retryTimes = 0
if resp.State == "done" {
fmt.Printf("worker %v map work done.", workerInfo.WorkId)
return
}
if resp.Filename == "" {
// 为空,但是没done,证明有问题了,等一秒重试
fmt.Println("map job assign done. but others workers are running")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
// 文件名获取没有问题
// deal with resp filename
// write to disk
req2 := MapTaskState{resp.Filename, workerInfo.WorkId, taskid, "done"}
resp2 := MapResponse{}
f, err := os.Open(resp.Filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
req2.State = "nosuchfile"
c.Call("Coordinator.MapTaskResp", &req2, &resp2)
continue
}
defer f.Close()
content, err := ioutil.ReadAll(f)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", resp.Filename)
req2.State = "filereaderr"
c.Call("Coordinator.MapTaskResp", &req2, &resp2)
}
kvs := mapf(resp.Filename, string(content))
// enc := json.NewEncoder(out)
encs := []*json.Encoder{}
midFiles = []*os.File{}
// 创建临时文件,确保执行完成了再重命名为mr-mid-{workid}-{taskid}_{nreduceid}
// 这样就算执行失败了或者重命名过程中执行失败了,存在的中间文件一定是对的
// reduce时nreduceid号相同的是同一个文件。
for i := 0; i < workerInfo.NReduce; i++ {
f, _ := os.CreateTemp("", "di-mp")
midFiles = append(midFiles, f)
}
for i := 0; i < workerInfo.NReduce; i++ {
encs = append(encs, json.NewEncoder(midFiles[i]))
}
for _, kv := range kvs {
encs[ihash(kv.Key)%workerInfo.NReduce].Encode(kv)
}
for i := 0; i < workerInfo.NReduce; i++ {
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d-%d_%d", "mr-mid", workerInfo.WorkId, taskid, i)
os.Rename(midFiles[i].Name(), name)
}
req2.Filename = resp.Filename
req2.TaskId = taskid
req2.State = "done"
err = c.Call("Coordinator.MapTaskResp", &req2, &resp2)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err: %v\n", err)
}
taskid++
// then send to MapTaskResp
// fmt.Printf("resp: %v\n", resp)
}
}
func WorkerReduce(reducef func(string, []string) string, client *rpc.Client) {
// 服务器运行完关闭或者网络有问题,重试
// 几次后退出
RESTARTREDUCE:
retryTimes := 0
for retryTimes < 3 {
req := ReduceRequest{}
var resp ReduceResponse
err2 := client.Call("Coordinator.AssignReduceTask", &req, &resp)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("err2: %v\n", err2)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
retryTimes++
continue
}
retryTimes = 0
if resp.State == "done" {
return
}
if resp.ReduceId == -1 {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Println("reduce job assign done. but others workers are running")
continue
}
// 至此,resp.Filename是中间文件的名字了
// 下一步,读取内容,排序,调用reduce。
// 类似串行的,只是这里是部分文件,传给
// coordinate之后再组合吧
req2 := ReduceTaskState{resp.ReduceId, ""}
resp2 := ReduceResponse{}
resp2.ReduceId = resp.ReduceId
fmt.Printf("worker id %v: %v\n", workerInfo.WorkId, resp.Filenames)
reduceId := resp2.ReduceId
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d", "mr-out", reduceId)
outtmpfile, _ := os.CreateTemp("", "di-out")
// outFile, _ = os.OpenFile(name, os.O_WRONLY|os.O_APPEND, 0666)
kva := []KeyValue{}
jsonParseState := true
for _, filename := range resp.Filenames {
f, err := os.Open(filename)
// fmt.Printf("resp.Filename: %v\n", resp.Filename)
defer f.Close()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("mid file open wrong:", err)
req2.State = "nosuchfile"
client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
goto RESTARTREDUCE
}
d := json.NewDecoder(f)
for {
var kv KeyValue
if err := d.Decode(&kv); err != nil {
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
fmt.Println("json parse:", err)
req2.State = "jsonparseerr"
client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
jsonParseState = false
break
}
// fmt.Printf("kv: %v\n", kv)
kva = append(kva, kv)
}
}
if jsonParseState {
sort.Sort(byKey(kva))
i := 0
for i < len(kva) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(kva) && kva[i].Key == kva[j].Key {
j++
}
vv := []string{}
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
vv = append(vv, kva[k].Value)
}
s := reducef(kva[i].Key, vv)
// 应当都行
fmt.Fprintf(outtmpfile, "%v %v\n", kva[i].Key, s)
// fmt.Fprintf(outFiles[ihash(kva[i].Key)%workerInfo.NReduce], "%v %v\n", kva[i].Key, s)
i = j
}
} else {
goto RESTARTREDUCE
}
req2.State = "done"
req2.ReduceId = resp.ReduceId
err := client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
if err == nil {
os.Rename(outtmpfile.Name(), name)
}
}
}
type byKey []KeyValue
func (a byKey) Len() int { return len(a) }
func (a byKey) Swap(i, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] }
func (a byKey) Less(i, j int) bool { return a[i].Key < a[j].Key }
//
// main/mrworker.go calls this function.
//
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,
reducef func(string, []string) string) {
// 定义一个uuid
i := 0
c, _ := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
defer c.Close()
c.Call("Coordinator.AssignWorkerId", &i, &workerInfo)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
WorkerMap(mapf, c)
// 至此,mid中间文件全部生成,可向coordinate请求中间文件名
// 按照mrsequential的做法
// 接下来就是请求一个中间文件,排序,计数,发送给coordinate
WorkerReduce(reducef, c)
}
//
// example function to show how to make an RPC call to the coordinator.
//
// the RPC argument and reply types are defined in rpc.go.
//
func CallExample() {
// declare an argument structure.
args := ExampleArgs{}
// fill in the argument(s).
args.X = 99
// declare a reply structure.
reply := ExampleReply{}
// send the RPC request, wait for the reply.
call("Coordinator.Example", &args, &reply)
// reply.Y should be 100.
fmt.Printf("reply.Y %v\n", reply.Y)
}
func clearMapMidFiles(midFiles []*os.File) {
for _, f := range midFiles {
f.Close()
os.Remove(f.Name())
}
}
//
// send an RPC request to the coordinator, wait for the response.
// usually returns true.
// returns false if something goes wrong.
//
func call(rpcname string, args interface{}, reply interface{}) bool {
c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
// sockname := coordinatorSock()
// c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("unix", sockname)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("dialing:", err)
}
defer c.Close()
err = c.Call(rpcname, args, reply)
if err == nil {
return true
}
fmt.Println(err)
return false
}
结果
hqinglau@centos:~/6.824/src/main$ bash test-mr.sh
*** Starting wc test.
--- wc test: PASS
--- indexer test: PASS
--- map parallelism test: PASS
--- reduce parallelism test: PASS
--- job count test: PASS
--- early exit test: FAIL
--- crash test: FAIL
两点,early eixt和crash test没过。
version 0.3
early exit
#########################################################
# test whether any worker or coordinator exits before the
# task has completed (i.e., all output files have been finalized)
echo '***' Starting early exit test.
ok,这个应该是退出信号给worker给早了。
在worker下面加一个等待的信号:
ret := false
for !ret {
err := c.Call("Coordinator.CoordinatorRPCDone", &i, &ret)
if err != nil {
break
}
}
当文件处理完毕时才是false:
func (c *Coordinator) CoordinatorRPCDone(i *int, ret *bool) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
t := c.ok
c.mtx.Unlock()
*ret = t
return nil
}
这个测试的时候报了一段错:
test-mr.sh: line 202: wait: -n: invalid option
wait: usage: wait [id]
sort: cannot read: mr-out*: No such file or directory
大概是这个命令在我的服务器上运行有问题:
# wait for any of the coord or workers to exit
# `jobs` ensures that any completed old processes from other tests
# are not waited upon
jobs &> /dev/null
wait -n # 这里报错了,直接就过去了,紧接着没有mr-out文件,还没执行创建呢
sort mr-out* | grep . > mr-wc-all-initial
这个是x年前新版本的特性,好吧,怪我版本太老。
我的是:
hqinglau@centos:~/6.824/src/main$ bash --version
GNU bash, version 4.2.46(2)-release (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu)
Copyright (C) 2011 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software; you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
OK,更新一下bash
$ bash --version
GNU bash, version 5.0.0(2)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
结果:
--- early exit test: PASS
好嘞,就剩一个崩溃检测了。
crash exit
这个应该分成两类大情况,一类是worker崩溃了,这个可以用定时任务搞。
一个是worker执行太慢或者网络问题,你以为它挂了,它还在慢慢跑。这个不附加另外操作,因为:就算慢慢跑,最后执行完了,临时文件重命名得到的也是正确的文件。。。卧槽。不是啊。没问题,执行完还是要发送给coordinator的,如果这个inputfile已经有别的worker搞定了,就不会加入mid文件列表,如果coordinator已经执行完关了,也不会影响到输出文件,重试几次后也就退出了。
总结一下,文件分出去之后要有定时器,超时要分配给别的worker;如果有两个worker执行一个task都执行完了,重复情况,判断完成的文件里是否已经存在,存在了就不管了。
代码:
func mapAfterFuncWrapper(c *Coordinator, filename string) func() {
return func() {
c.mtx.Lock()
fmt.Printf("map task %v 超时重试\n", filename)
c.files = append(c.files, filename)
c.mtx.Unlock()
}
}
func reduceAfterFuncWrapper(c *Coordinator, reduceId int) func() {
return func() {
c.mtx.Lock()
fmt.Printf("reduce task %v 超时重试\n", reduceId)
c.midFilesList = append(c.midFilesList, reduceId)
c.mtx.Unlock()
}
}
// map调用,返回第一个文件名
func (c *Coordinator) AssignMapTask(req *MapRequest, resp *MapResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.files) == 0 {
resp.Filename = ""
if len(c.mapSend) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
fmt.Println("map task done.")
}
} else {
resp.Filename = c.files[0]
c.files = c.files[1:]
f := mapAfterFuncWrapper(c, resp.Filename)
c.mapSend[resp.Filename] = time.AfterFunc(time.Second*10, f)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
// fmt.Printf("c.files: %v\n", c.files)
fmt.Printf("c.files: %v\n", c.files)
fmt.Printf("c.mapSend: %v\n", c.mapSend)
return nil
}
// reduce之前,返回中间文件的文件名d
func (c *Coordinator) AssignReduceTask(req *ReduceRequest, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.midFilesList) == 0 {
resp.Filenames = nil
resp.ReduceId = -1
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
fmt.Println("reduce task done")
}
} else {
resp.ReduceId = c.midFilesList[0]
c.midFilesList = c.midFilesList[1:]
resp.Filenames = c.midFilesMap[resp.ReduceId]
f := reduceAfterFuncWrapper(c, resp.ReduceId)
c.reduceSend[resp.ReduceId] = time.AfterFunc(time.Second*10, f)
}
fmt.Printf("c.midFilesList: %v\n", c.midFilesList)
fmt.Printf("c.reduceSend: %v\n", c.reduceSend)
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
草,搞半天还没pass,原来是go func里面没加锁的原因,另外一个协程,二者都要处理coordinator的数据,需要加锁。
time.AfterFunc参数传递
里面要传递函数,但是afterFunc默认是参数没有的,所以需要一层wrapper,把参数包进去:
func reduceAfterFuncWrapper(c *Coordinator, reduceId int) func() {
return func() {
c.mtx.Lock()
fmt.Printf("reduce task %v 超时重试\n", reduceId)
c.midFilesList = append(c.midFilesList, reduceId)
c.mtx.Unlock()
}
}
// 使用
f := reduceAfterFuncWrapper(c, resp.ReduceId)
c.reduceSend[resp.ReduceId] = time.AfterFunc(time.Second*10, f)
ALL PASS
--- crash test: PASS
*** PASSED ALL TESTS
全过了,OK。
总结
这个lab1就先这样,经验都在上文记录的心理历程里了,还是花了些时间才搞完的。Next one.